Chlorine is poisonous, but sodium chloride is essential to life; sodium atoms react vigorously with water, but sodium chloride simply dissolves in water. Figure 7.3.1 7.3. 1: (a) Sodium is a soft metal that must be stored in mineral oil to prevent reaction with air or water. (b) Chlorine is a pale yellow-green gas.
Welcome to Chem Zipper.com……: What is structure (CF3)2-Al-O-Al-(CF3)2 and also find the number of pi bond or Back bond?
Bond Strength: Covalent Bonds. Stable molecules exist because covalent bonds hold the atoms together. We measure the strength of a covalent bond by the energy required to break it, that is, the energy necessary to separate the bonded atoms. Separating any pair of bonded atoms requires energy (see Figure 1).
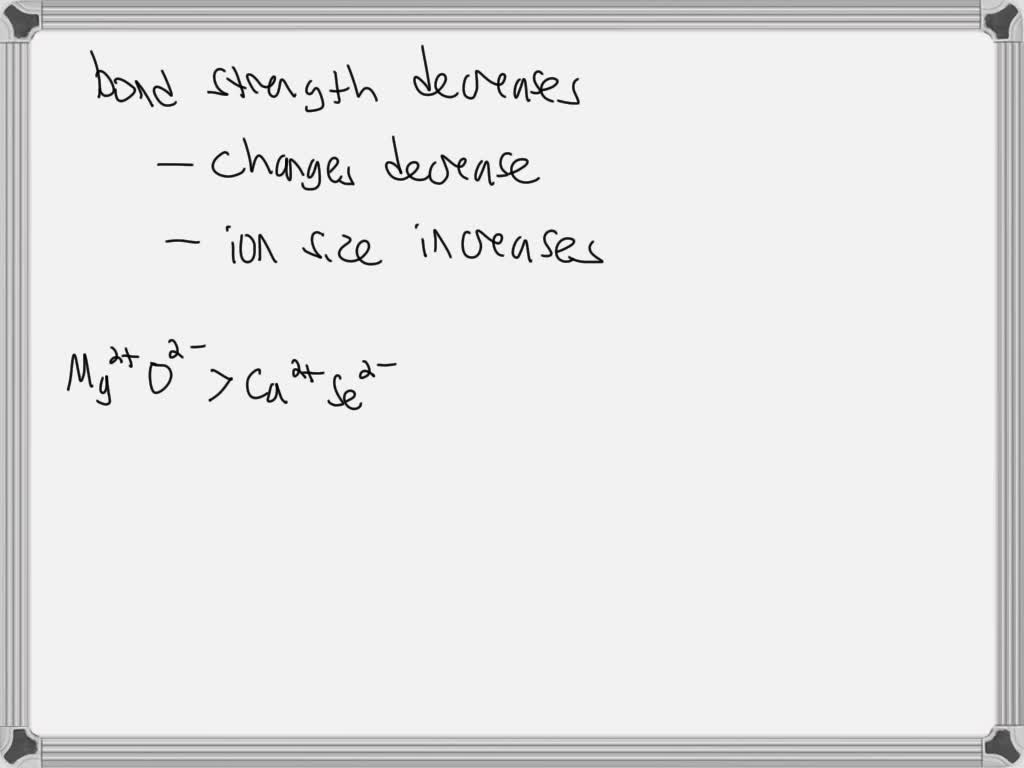
Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
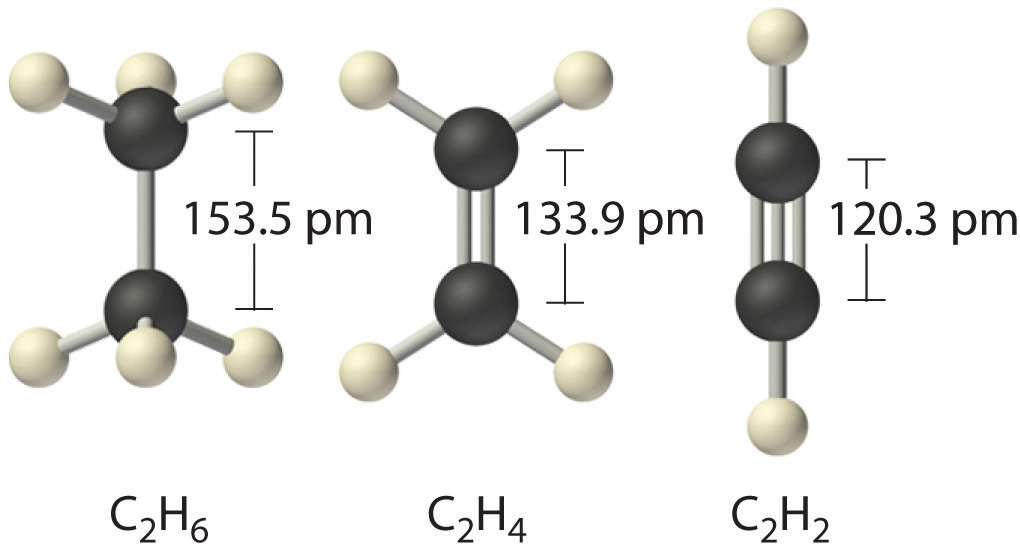
Jan 30, 2023Bond order is the number of chemical bonds between a pair of atoms and indicates the stability of a bond. For example, in diatomic nitrogen, N≡N, the bond order is 3; in acetylene, H−C≡C−H, the carbon-carbon bond order is also 3, and the C−H bond order is 1. Bond order and bond length indicate the type and strength of covalent bonds

Source Image: scribd.com
Download Image
Properties of Covalent Bonds VIDEO ANSWER: To order these ion pairs by decreasing bond strength, we need to recognize that the bond strength decreasesas a general rule of thumb, as 2 things occur, charges decrease and ion size increases, so we’re going to order them from
Source Image: pubs.rsc.org
Download Image
Order The Following Ion Pairs By Decreasing Bond Strength.
VIDEO ANSWER: To order these ion pairs by decreasing bond strength, we need to recognize that the bond strength decreasesas a general rule of thumb, as 2 things occur, charges decrease and ion size increases, so we’re going to order them from the bonds in each set in order of decreasing bond length and decreasing bond strength: (a) S-F, S-Br, S-Cl (b) C=O, C-O, CΞO . PLAN: (a) S is singly bonded to three different halogen atoms, so the bond order is the same. Bond length increases and bond strength decreases as the atomic radius of the halogen increases.
MOF catalysis meets biochemistry: molecular insights from the hydrolytic activity of MOFs towards biomolecules – Molecular Systems Design & Engineering (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/D2ME00213B
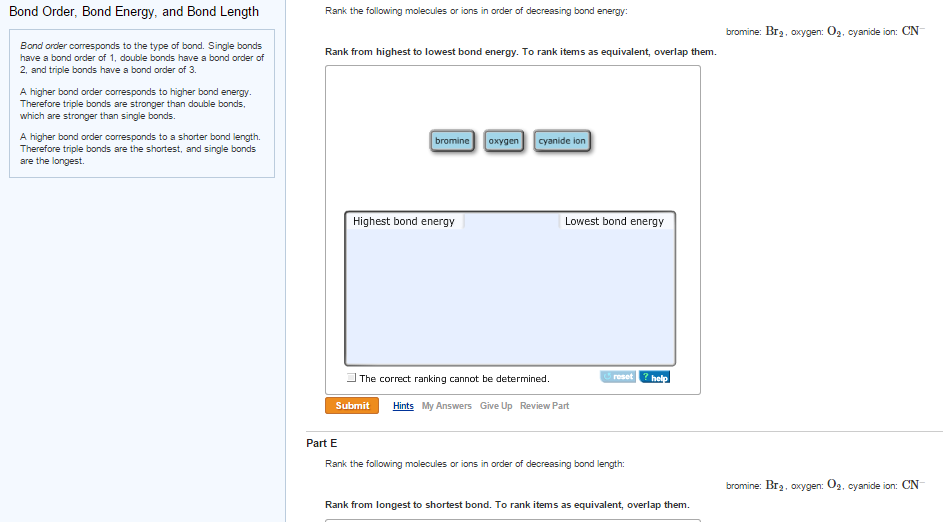
Question: Strongest Mg2+ O2- Order the following ion pairs by decreasing bond strength. (Strongest to weakest: left to right.) … Strongest Mg2+ O2- Order the following ion pairs by decreasing bond strength. (Strongest to weakest: left to right.) Lit F- > Ca²+ O²- V Nat Br V Ca²+ Se²- Nat F- V Weakest. Show transcribed image text. There Solved Bond Order, Bond Energy, and Bond Length Rank the | Chegg.com
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
Rank the indicated bond in the given compound in order of decreasing bond strength: (A) \( abc \… – YouTube Question: Strongest Mg2+ O2- Order the following ion pairs by decreasing bond strength. (Strongest to weakest: left to right.) … Strongest Mg2+ O2- Order the following ion pairs by decreasing bond strength. (Strongest to weakest: left to right.) Lit F- > Ca²+ O²- V Nat Br V Ca²+ Se²- Nat F- V Weakest. Show transcribed image text. There

Source Image: youtube.com
Download Image
Welcome to Chem Zipper.com……: What is structure (CF3)2-Al-O-Al-(CF3)2 and also find the number of pi bond or Back bond? Chlorine is poisonous, but sodium chloride is essential to life; sodium atoms react vigorously with water, but sodium chloride simply dissolves in water. Figure 7.3.1 7.3. 1: (a) Sodium is a soft metal that must be stored in mineral oil to prevent reaction with air or water. (b) Chlorine is a pale yellow-green gas.

Source Image: chemzipper.com
Download Image
Properties of Covalent Bonds Jan 30, 2023Bond order is the number of chemical bonds between a pair of atoms and indicates the stability of a bond. For example, in diatomic nitrogen, N≡N, the bond order is 3; in acetylene, H−C≡C−H, the carbon-carbon bond order is also 3, and the C−H bond order is 1. Bond order and bond length indicate the type and strength of covalent bonds
Source Image: 2012books.lardbucket.org
Download Image
Chemical Bonding | PDF Sep 22, 2022Average bond energies for some common bonds appear in Table 7.5.2 7.5. 2, and a comparison of bond lengths and bond strengths for some common bonds appears in Table 7.5.2 7.5. 2. When one atom bonds to various atoms in a group, the bond strength typically decreases as we move down the group. For example, C-F is 439 kJ/mol, C-Cl is 330 kJ

Source Image: scribd.com
Download Image
Which one of the following represents the INCORRECT decreasing order of bond angles ? – Sarthaks eConnect | Largest Online Education Community VIDEO ANSWER: To order these ion pairs by decreasing bond strength, we need to recognize that the bond strength decreasesas a general rule of thumb, as 2 things occur, charges decrease and ion size increases, so we’re going to order them from

Source Image: sarthaks.com
Download Image
Exploring Coal by NEED Project – Issuu the bonds in each set in order of decreasing bond length and decreasing bond strength: (a) S-F, S-Br, S-Cl (b) C=O, C-O, CΞO . PLAN: (a) S is singly bonded to three different halogen atoms, so the bond order is the same. Bond length increases and bond strength decreases as the atomic radius of the halogen increases.

Source Image: issuu.com
Download Image
Rank the indicated bond in the given compound in order of decreasing bond strength: (A) \( abc \… – YouTube
Exploring Coal by NEED Project – Issuu Bond Strength: Covalent Bonds. Stable molecules exist because covalent bonds hold the atoms together. We measure the strength of a covalent bond by the energy required to break it, that is, the energy necessary to separate the bonded atoms. Separating any pair of bonded atoms requires energy (see Figure 1).
Properties of Covalent Bonds Which one of the following represents the INCORRECT decreasing order of bond angles ? – Sarthaks eConnect | Largest Online Education Community Sep 22, 2022Average bond energies for some common bonds appear in Table 7.5.2 7.5. 2, and a comparison of bond lengths and bond strengths for some common bonds appears in Table 7.5.2 7.5. 2. When one atom bonds to various atoms in a group, the bond strength typically decreases as we move down the group. For example, C-F is 439 kJ/mol, C-Cl is 330 kJ