Jul 12, 2023Fermentation is an anaerobic process of breaking down organic molecules. It occurs in the absence of oxygen. Fermentation breaks down organic molecules, such as glucose, into smaller organic molecule end products. Fermentation begins with the process of glycolysis to produce pyruvic acid and 2 net ATP.
25 Chapter 9: Cell Respiration and Fermentation ideas | cell respiration, biology, teaching biology
Lesson 6: Variations on cellular respiration. Lactic acid fermentation. Alcohol or ethanol fermentation. Fermentation and anaerobic respiration. Connections between cellular respiration and other pathways. Science >. Biology library >. Cellular respiration.

Source Image: slideshare.net
Download Image
Aerobic fermentation. Aerobic fermentation or aerobic glycolysis is a metabolic process by which cells metabolize sugars via fermentation in the presence of oxygen and occurs through the repression of normal respiratory metabolism. Preference of aerobic fermentation over aerobic respiration is referred to as the Crabtree effect in yeast, [1] [2

Source Image: pinterest.com
Download Image
Difference Between Aerobic and Anaerobic Fermentation – Pediaa.Com Many bacteria and yeasts carry out fermentation. People use these organisms to make yogurt, bread, wine, and biofuels. Human muscle cells also use fermentation. This occurs when muscle cells cannot get oxygen fast enough to meet their energy needs through aerobic respiration. There are two types of fermentation: lactic acid fermentation and

Source Image: collegedunia.com
Download Image
Sequence Events That Lead To Fermentation In Aerobic Organisms
Many bacteria and yeasts carry out fermentation. People use these organisms to make yogurt, bread, wine, and biofuels. Human muscle cells also use fermentation. This occurs when muscle cells cannot get oxygen fast enough to meet their energy needs through aerobic respiration. There are two types of fermentation: lactic acid fermentation and Cellular Respiration. Cellular respiration is the set of the metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and then release waste products. The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions, which break large molecules into
Respiration in Organisms: Definition and Types
Table 8.2 Microbial fermentation processes have been manipulated by humans and are used extensively in the production of various foods and other commercial products, including pharmaceuticals. Microbial fermentation can also be useful for identifying microbes for diagnostic purposes. Sequential dark–photo fermentation and autotrophic microalgal growth for high-yield and CO2-free biohydrogen production – ScienceDirect

Source Image: sciencedirect.com
Download Image
Understanding Anaerobic Respiration: Process, Benefits, and Examples Table 8.2 Microbial fermentation processes have been manipulated by humans and are used extensively in the production of various foods and other commercial products, including pharmaceuticals. Microbial fermentation can also be useful for identifying microbes for diagnostic purposes.

Source Image: pinterest.com
Download Image
25 Chapter 9: Cell Respiration and Fermentation ideas | cell respiration, biology, teaching biology Jul 12, 2023Fermentation is an anaerobic process of breaking down organic molecules. It occurs in the absence of oxygen. Fermentation breaks down organic molecules, such as glucose, into smaller organic molecule end products. Fermentation begins with the process of glycolysis to produce pyruvic acid and 2 net ATP.

Source Image: pinterest.com
Download Image
Difference Between Aerobic and Anaerobic Fermentation – Pediaa.Com Aerobic fermentation. Aerobic fermentation or aerobic glycolysis is a metabolic process by which cells metabolize sugars via fermentation in the presence of oxygen and occurs through the repression of normal respiratory metabolism. Preference of aerobic fermentation over aerobic respiration is referred to as the Crabtree effect in yeast, [1] [2

Source Image: pediaa.com
Download Image
Sequence events that lead to fermentation in aerobic organisms. | bartleby Steps of cellular respiration. During cellular respiration, a glucose molecule is gradually broken down into carbon dioxide and water. Along the way, some ATP is produced directly in the reactions that transform glucose. Much more ATP, however, is produced later in a process called oxidative phosphorylation. Oxidative phosphorylation is powered
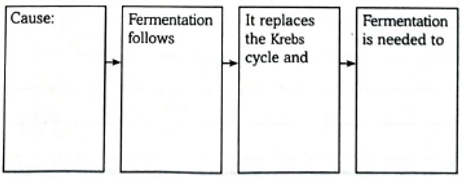
Source Image: bartleby.com
Download Image
Anaerobic Respiration | Definition, Equation & Types – Lesson | Study.com Many bacteria and yeasts carry out fermentation. People use these organisms to make yogurt, bread, wine, and biofuels. Human muscle cells also use fermentation. This occurs when muscle cells cannot get oxygen fast enough to meet their energy needs through aerobic respiration. There are two types of fermentation: lactic acid fermentation and

Source Image: study.com
Download Image
Bacterial metabolism by fermentation (A) and aerobic aspiration (B)…. | Download Scientific Diagram Cellular Respiration. Cellular respiration is the set of the metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and then release waste products. The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions, which break large molecules into

Source Image: researchgate.net
Download Image
Understanding Anaerobic Respiration: Process, Benefits, and Examples
Bacterial metabolism by fermentation (A) and aerobic aspiration (B)…. | Download Scientific Diagram Lesson 6: Variations on cellular respiration. Lactic acid fermentation. Alcohol or ethanol fermentation. Fermentation and anaerobic respiration. Connections between cellular respiration and other pathways. Science >. Biology library >. Cellular respiration.
Difference Between Aerobic and Anaerobic Fermentation – Pediaa.Com Anaerobic Respiration | Definition, Equation & Types – Lesson | Study.com Steps of cellular respiration. During cellular respiration, a glucose molecule is gradually broken down into carbon dioxide and water. Along the way, some ATP is produced directly in the reactions that transform glucose. Much more ATP, however, is produced later in a process called oxidative phosphorylation. Oxidative phosphorylation is powered