The mastoid process is a small triangular-shaped bone that protrudes from either side at the base of your skull. You can locate your mastoid if you place your fingers behind your earlobe. The main function of the mastoid process is to connect your neck muscles to your skull and help regulate pressure in your ear.
Cureus | The Radiological Evaluation of the Mastoid Process and Its Implications for Surgical Approaches | Article
Determine which of the following structures cannot normally be palpated on a living person: the mastoid process, crista galli, superior orbital fissure, palatine processes, zygomatic bone, mental protuberance, and stapes. You may find it useful to palpate some of these on your own skull as you try to answer. Solution Verified Answered 2 years ago

Source Image: caringmedical.com
Download Image
Jun 21, 2023The mastoid process is a bony projection at the base of the temporal bones on each side of the skull. The mastoid processes can be felt behind the ear lobes. This structure is an attachment point for several head and neck muscles. It also contains air cells that help drain fluid from the middle ear.

Source Image: shutterstock.com
Download Image
Bony Landmark Palpation – Temporal Bone (Skull) – YouTube Jun 24, 2023VIDEO ANSWER: This question here says, determine which of the following structures cannot normally be palpated on a living person. You have the mastoid process, the crista galli, the superior orbital fissure, the p
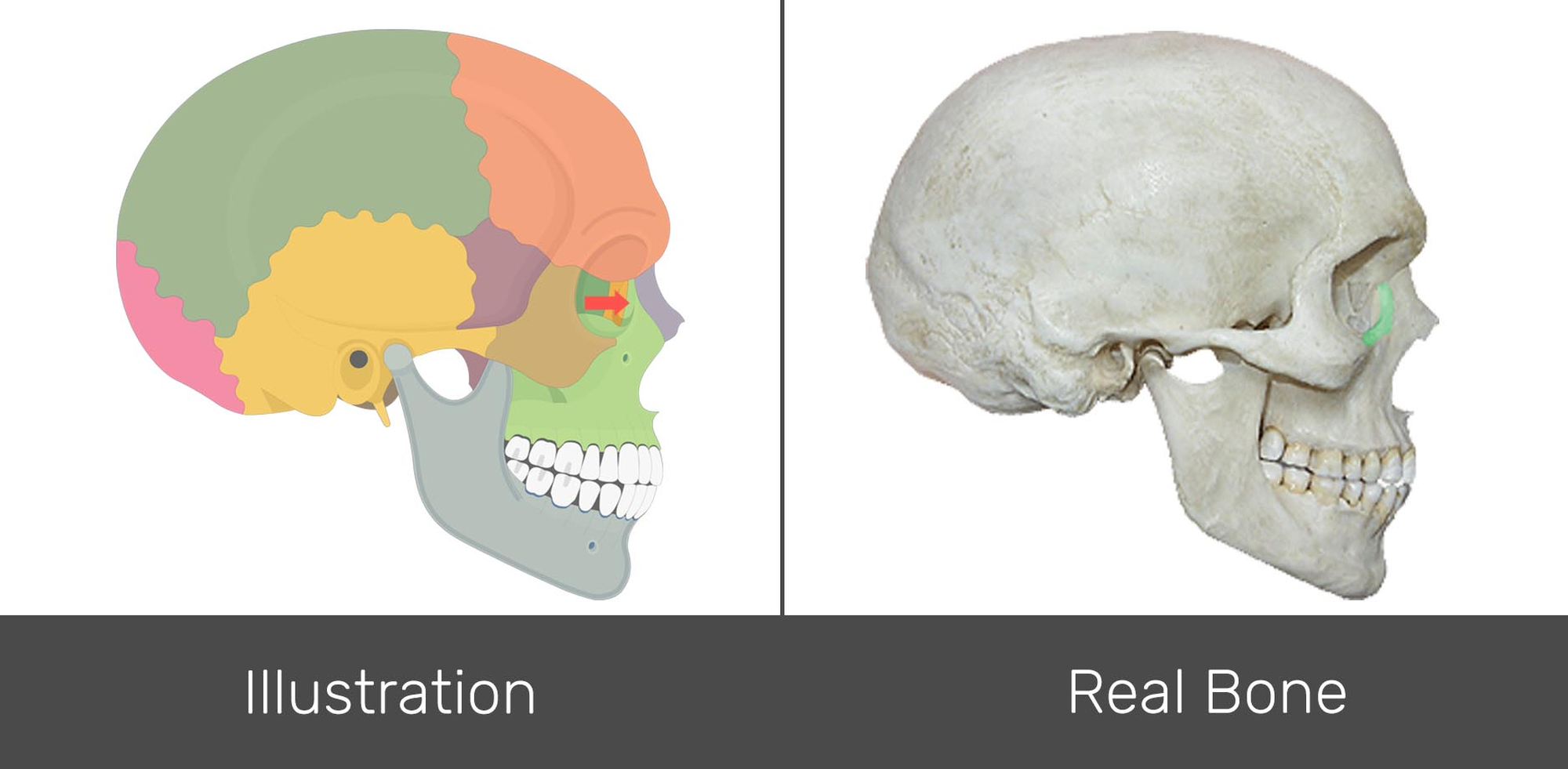
Source Image: getbodysmart.com
Download Image
The Mastoid Process Cannot Be Palpated On A Living Person
Jun 24, 2023VIDEO ANSWER: This question here says, determine which of the following structures cannot normally be palpated on a living person. You have the mastoid process, the crista galli, the superior orbital fissure, the p Etymology. The word “mastoid” is derived from the Greek word for “breast”, a reference to the shape of this bone.Surfaces Mastoid process shown in red Outer surface. Its outer surface is rough and gives attachment to the occipitalis and posterior auricular muscles.It is perforated by numerous foramina (holes); for example, the mastoid foramen is situated near the posterior border and transmits
Skull Quiz – Lateral View | GetBodySmart
May 25, 2023The mastoid process is easily palpable just behind the ears. It serves as the insertion site of many muscles in the head and neck region. In addition, it contains air-filled spaces called the mastoid air cells . This article will discuss the gross and functional anatomy of the mastoid process . Contents Borders and relations Muscle attachements MS2 Ears | PDF | Ear | Vertigo

Source Image: scribd.com
Download Image
84 Mastoid Process Images, Stock Photos, 3D objects, & Vectors | Shutterstock May 25, 2023The mastoid process is easily palpable just behind the ears. It serves as the insertion site of many muscles in the head and neck region. In addition, it contains air-filled spaces called the mastoid air cells . This article will discuss the gross and functional anatomy of the mastoid process . Contents Borders and relations Muscle attachements

Source Image: shutterstock.com
Download Image
Cureus | The Radiological Evaluation of the Mastoid Process and Its Implications for Surgical Approaches | Article The mastoid process is a small triangular-shaped bone that protrudes from either side at the base of your skull. You can locate your mastoid if you place your fingers behind your earlobe. The main function of the mastoid process is to connect your neck muscles to your skull and help regulate pressure in your ear.
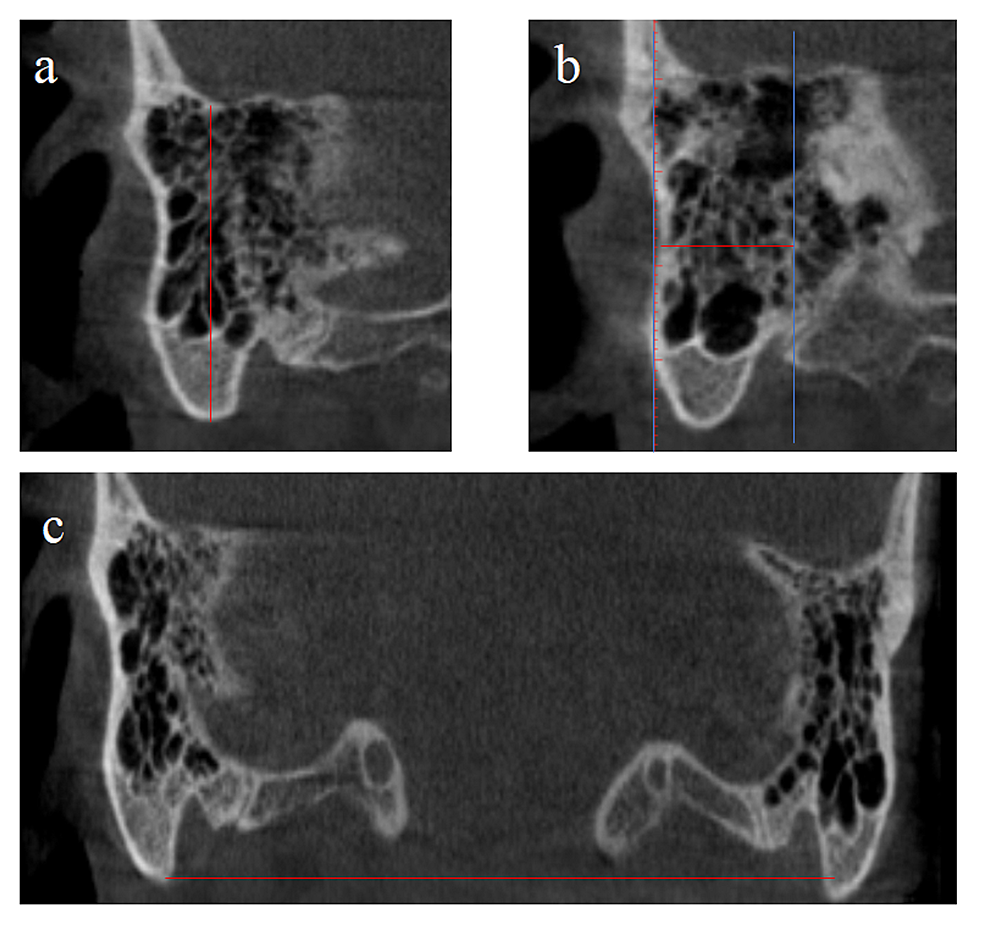
Source Image: cureus.com
Download Image
Bony Landmark Palpation – Temporal Bone (Skull) – YouTube Jun 21, 2023The mastoid process is a bony projection at the base of the temporal bones on each side of the skull. The mastoid processes can be felt behind the ear lobes. This structure is an attachment point for several head and neck muscles. It also contains air cells that help drain fluid from the middle ear.
Source Image: m.youtube.com
Download Image
ArtStation – Mastoid process, Anatomy For Sculptors | Human anatomy drawing, Face anatomy, Human muscle anatomy Mastoiditis. Mastoiditis is a bacterial infection of the mastoid air cells, which typically occurs after acute otitis media. Symptoms include redness, tenderness, swelling, and fluctuation over the mastoid process, with displacement of the pinna. Diagnosis is clinical. Treatment is with antibiotics, such as ceftriaxone, and, if antibiotics

Source Image: pinterest.com
Download Image
Nonsyndromic Single Suture Craniosynostosis | Pocket Dentistry Jun 24, 2023VIDEO ANSWER: This question here says, determine which of the following structures cannot normally be palpated on a living person. You have the mastoid process, the crista galli, the superior orbital fissure, the p
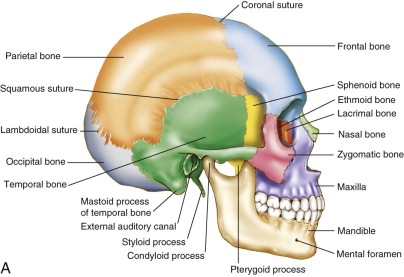
Source Image: pocketdentistry.com
Download Image
Mastoid Process | PPT Etymology. The word “mastoid” is derived from the Greek word for “breast”, a reference to the shape of this bone.Surfaces Mastoid process shown in red Outer surface. Its outer surface is rough and gives attachment to the occipitalis and posterior auricular muscles.It is perforated by numerous foramina (holes); for example, the mastoid foramen is situated near the posterior border and transmits

Source Image: slideshare.net
Download Image
84 Mastoid Process Images, Stock Photos, 3D objects, & Vectors | Shutterstock
Mastoid Process | PPT Determine which of the following structures cannot normally be palpated on a living person: the mastoid process, crista galli, superior orbital fissure, palatine processes, zygomatic bone, mental protuberance, and stapes. You may find it useful to palpate some of these on your own skull as you try to answer. Solution Verified Answered 2 years ago
Bony Landmark Palpation – Temporal Bone (Skull) – YouTube Nonsyndromic Single Suture Craniosynostosis | Pocket Dentistry Mastoiditis. Mastoiditis is a bacterial infection of the mastoid air cells, which typically occurs after acute otitis media. Symptoms include redness, tenderness, swelling, and fluctuation over the mastoid process, with displacement of the pinna. Diagnosis is clinical. Treatment is with antibiotics, such as ceftriaxone, and, if antibiotics